
문제
요즘 많은 자동차에서는 GPS 네비게이션 장비가 설치되어 있다. 네비게이션은 사용자가 입력한 출발점과 도착점 사이의 최단 경로를 검색해 준다. 하지만, 교통 상황을 고려하지 않고 최단 경로를 검색하는 경우에는 극심한 교통 정체를 경험할 수 있다.
상근이는 오직 자기 자신만 사용 가능한 네비게이션을 만들고 있다. 이 네비게이션은 절대로 최단 경로를 찾아주지 않는다. 항상 거의 최단 경로를 찾아준다.
거의 최단 경로란 최단 경로에 포함되지 않는 도로로만 이루어진 경로 중 가장 짧은 것을 말한다.
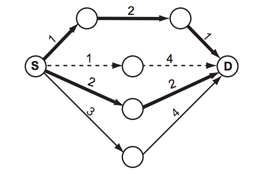
예를 들어, 도로 지도가 아래와 같을 때를 생각해보자. 원은 장소를 의미하고, 선은 단방향 도로를 나타낸다. 시작점은 S, 도착점은 D로 표시되어 있다. 굵은 선은 최단 경로를 나타낸다. (아래 그림에 최단 경로는 두 개가 있다)거의 최단 경로는 점선으로 표시된 경로이다. 이 경로는 최단 경로에 포함되지 않은 도로로 이루어진 경로 중 가장 짧은 경로이다. 거의 최단 경로는 여러 개 존재할 수도 있다. 예를 들어, 아래 그림의 길이가 3인 도로의 길이가 1이라면, 거의 최단 경로는 두 개가 된다. 또, 거의 최단 경로가 없는 경우도 있다.
입력
입력은 여러 개의 테스트 케이스로 이루어져 있다. 각 테스트 케이스의 첫째 줄에는 장소의 수 N (2 ≤ N ≤ 500)과 도로의 수 M (1 ≤ M ≤ 104)가 주어진다. 장소는 0부터 N-1번까지 번호가 매겨져 있다. 둘째 줄에는 시작점 S와 도착점 D가 주어진다. (S ≠ D; 0 ≤ S, D < N) 다음 M개 줄에는 도로의 정보 U, V, P가 주어진다. (U ≠ V ; 0 ≤ U, V < N; 1 ≤ P ≤ 103) 이 뜻은 U에서 V로 가는 도로의 길이가 P라는 뜻이다. U에서 V로 가는 도로는 최대 한 개이다. 또, U에서 V로 가는 도로와 V에서 U로 가는 도로는 다른 도로이다.
입력의 마지막 줄에는 0이 두 개 주어진다.
출력
각 테스트 케이스에 대해서, 거의 최단 경로의 길이를 출력한다. 만약, 거의 최단 경로가 없는 경우에는 -1을 출력한다.
풀이 과정
먼저, s -> d로 향하는 최단 경로를 구했다. 최단 경로를 구하면서 최단 경로로 향하는 중에 지나는 도로 정보를 수집했다.
dijkstra 함수의 distances_path 가 그 정보를 수집한다.
1. 만약 지금까지 최단 경로보다 더 빠른 최단 경로가 있다면 next_destination의 도로 정보를 초기화한 후, current_destination까지의 최단 경로 도로 정보를 담고 current_destination -> next_destination 의 도로 정보를 담았다..
2. 만약 지금까지 최단 경로와 같은 최단 경로가 있다면 currnet_destination까지의 최단 경로 도로 정보를 더한다. ( set를 사용하여 중복을 막았다. )
최단 경로를 찾았다면, 최단 경로로 향하는 중에 지나는 도로 정보를 graph 에서 모두 삭제한다.
그 후 최단 거리만 구하는 다익스트라 함수 (dijkstra_dist)를 다시 작성하여 목적지까지의 최단 거리를 구해 출력했다.
import sys
import heapq
input = sys.stdin.readline
def dijkstra(city_num, start):
distances = [float('inf') for _ in range(city_num)]
distances[start] = 0
distances_path = [set() for _ in range(city_num)]
queue = []
heapq.heappush(queue, (0, start))
while queue:
current_distance, current_destination = heapq.heappop(queue)
if distances[current_destination] < current_distance: continue
for next_destination, next_distance in graph[current_destination].items():
if current_distance + next_distance <= distances[next_destination]:
if current_distance + next_distance < distances[next_destination]:
distances[next_destination] = current_distance + next_distance
distances_path[next_destination] = set()
heapq.heappush(queue, (current_distance + next_distance, next_destination))
now_path = "%d_%d"%(current_destination, next_destination)
if len(distances_path[current_destination]) > 0:
for i in distances_path[current_destination]:
distances_path[next_destination].add(i)
distances_path[next_destination].add(now_path)
return distances, distances_path
def dijkstra_dist(city_num, start):
distances = [float('inf') for _ in range(city_num)]
distances[start] = 0
queue = []
heapq.heappush(queue, (0, start))
while queue:
current_distance, current_destination = heapq.heappop(queue)
if distances[current_destination] < current_distance: continue
for next_destination, next_distance in graph[current_destination].items():
if current_distance + next_distance < distances[next_destination]:
distances[next_destination] = current_distance + next_distance
heapq.heappush(queue, (current_distance + next_distance, next_destination))
return distances
while True:
n, m = map(int, input().rstrip().split())
if n == m == 0: break
s, d = map(int, input().rstrip().split())
graph = [{} for _ in range(n)]
for _ in range(m):
u, v, p = map(int, input().rstrip().split())
graph[u][v] = p
# 1. 최단 경로 구하기
result, result_path = dijkstra(n, s)
# 2. 최단 경로에 포함된 도로 지우기
for now_path in result_path[d]:
left, right = map(int, now_path.split('_'))
if graph[left].get(right):
del graph[left][right]
# 3. 다시 최단 경로 구하기
result = dijkstra_dist(n, s)
print(result[d] if result[d] != float('inf') else -1)'-- 예전 기록 > BOJ' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ BOJ ] 2662 : 기업투자 ( GOLD 2 ) / Python (0) | 2023.10.03 |
|---|---|
| [ BOJ ] 5582 : 공통 부분 문자열 ( GOLD 5 ) / Python (0) | 2023.10.03 |
| [ BOJ ] 2908 : 상수 ( BRONZE 2 ) / C, C++, Python, Java (0) | 2023.10.03 |
| [ BOJ ] 6825 : Body Mass Index ( BRONZE 4 ) / C, Python (0) | 2023.10.03 |
| [ BOJ ] 19602 : Dog Treats ( BRONZE 4 ) / C, Python (0) | 2023.10.03 |